HEALTH BELIEF MODEL
KEY CONCEPTS
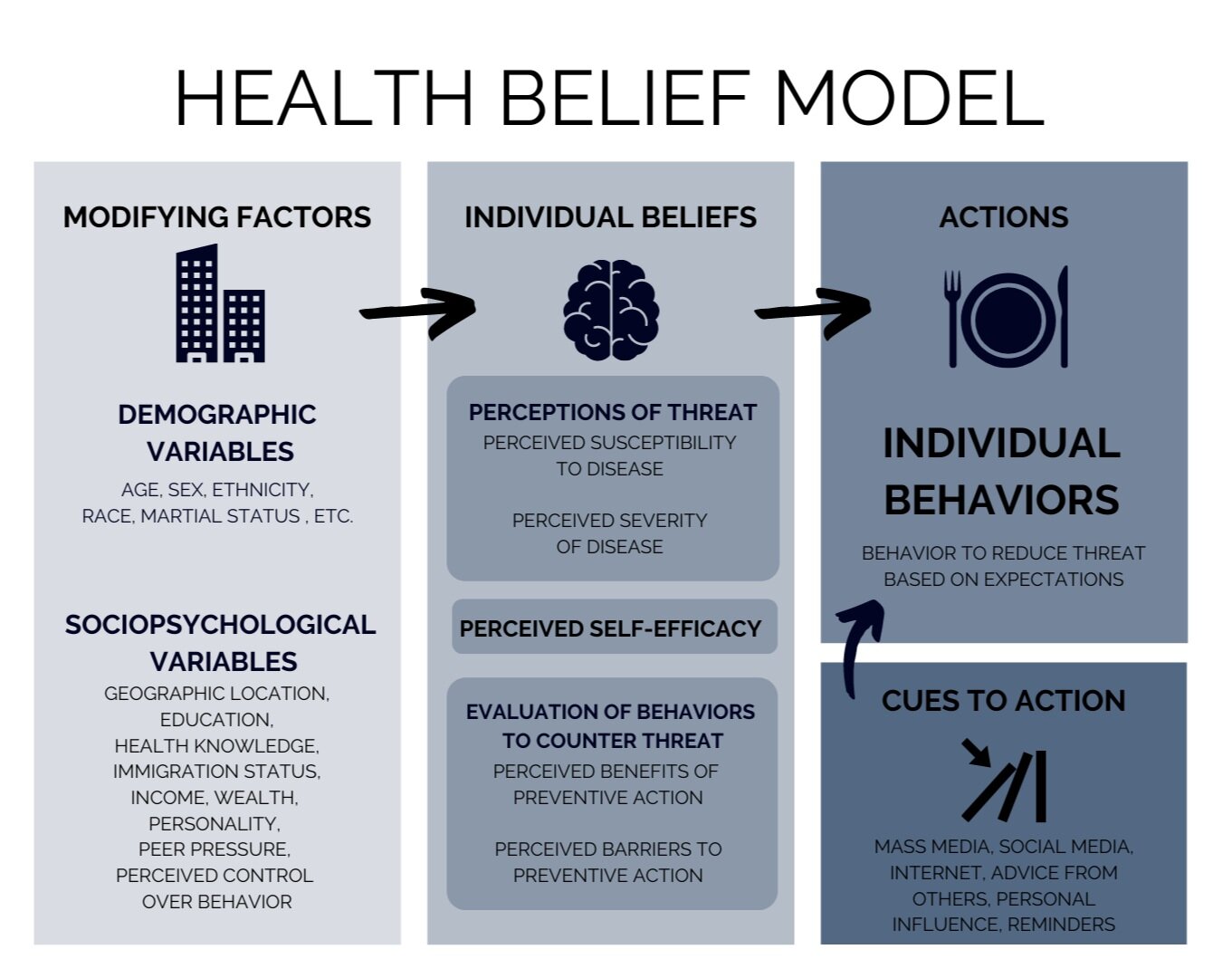
An individual’s belief system influences their decision making and the ability to maintain specific health behavior changes.
To make a health behavior change an individual may have one or several of these factors to influence whether they will or will not make a change:
PERCEIVED SUSCEPTIBILITY: They believe that they are likely and/or capable of getting a disease or condition.
PERCEIVED SEVERITY: They believe that the disease or condition is dangerous and can highly affect them.
PERCEIVED BENEFITS: They believe that taking action will provide them benefits to prevent or cure the disease or condition.
PERCEIVED BARRIERS: They believe that either there are no major barriers to the behavior change or that there are major barriers to change.
SELF-EFFICACY: They believe that they are able to do the behavior.
CUES TO ACTION: They are triggered by an outside influence that encourages them to take action.
When a person believes he or she is susceptible to a health problem with sever consequences, the person will more likely conclude that the benefits outweigh the barriers.
KEY TERMS
PERCEIVE [def]: To become aware or conscious of (something); come to realize or understand.
SELF-EFFICACY [def]: is a person's belief in their ability to succeed in a particular situation.
REFERENCES:
Becker MH. The Health Belief Model and personal health behavior. Health Education Monographs. 1974;2:324–508.
Rosenstock IM, Strecher V, Becker J. Social learning theory and the health belief model. Health Education Quarterly. 1988;15:175–183. doi: 10.1177/109019818801500203